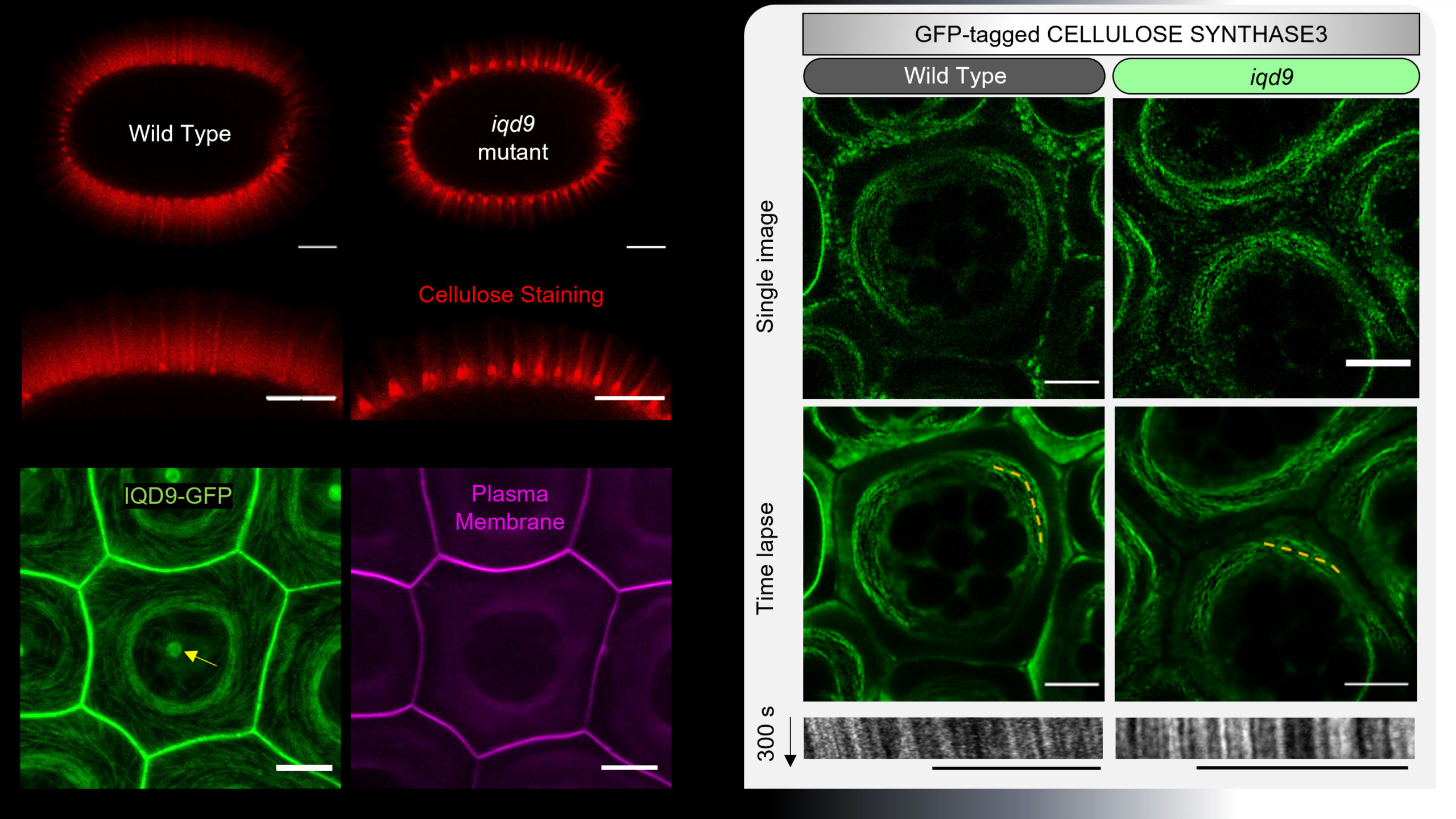
In our new pre-print, we explore two outstanding questions that have been challenging to address in plant cells: What proteins control the microtubule cytoskeleton and how do they function together to influence the polarized deposition of complex polysaccharides in the cell wall?
Using Arabidopsis seed coat epidermal cells as a genetic model system, we discovered that IQ67 DOMAIN 9 (IQD9) and KINESIN LIGHT CHAIN-RELATED 1 (KLCR1) have overlapping roles in microtubule organization and cellulose deposition with the TONNEAU1 (TON1) RECRUITING MOTIF 4 (TRM4) protein we previously identified (Yang et al., 2019; New Phytologist).
Our results demonstrate that IQD9, KLCR1 and TRM4 are microtubule-associated proteins that modulate seed mucilage architecture by supporting cellulose synthase movement. This study provides the first direct evidence that members of these three families have overlapping roles in cell wall biosynthesis.
References
Yang B, Stamm G, Bürstenbinder K*, Voiniciuc C*. Microtubule-associated IQD9 guides cellulose synthase velocity to shape seed mucilage. bioRxiv: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.11.472226
Yang et al., 2019; New Phytologist: https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15442